What Is Marketing?
Marketing is the process of promoting, selling, and distributing a product or service to the target audience. It involves understanding customer needs, creating valuable products, and effectively communicating their benefits. Marketing is a bridge that connects businesses with potential customers, ensuring mutual value creation and satisfaction.
In today’s competitive business landscape, marketing has expanded beyond traditional methods. It now incorporates digital platforms, data analytics, and customer-centric strategies to achieve optimal results.
Key Takeaways
- Marketing is essential for growth: It helps businesses identify their audience, understand their needs, and tailor products or services accordingly.
- It builds relationships: Marketing fosters trust, loyalty, and long-term connections with customers by delivering consistent value.
- Marketing drives visibility: Through effective strategies, it positions brands where their audience is most active, whether online or offline.
- Multi-faceted discipline: Marketing combines elements of creativity, technology, and data analysis to create impactful campaigns.
- Adapts to changing trends: Marketing evolves with consumer behavior, technological advancements, and global economic shifts.

Formal Definition
Marketing, as defined by the American Marketing Association (AMA), is the “activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.”
This definition highlights three key components:
- Value Creation: The core of marketing is to deliver value. Whether it’s a product, service, or experience, the focus is always on addressing customer needs effectively.
- Communication: Marketing involves clear and persuasive communication to inform customers about the value proposition of a product or service.
- Exchange of Offerings: It facilitates the exchange between businesses and customers, ensuring mutual benefit.
Example in Practice: A small business might create a marketing campaign showcasing the unique features of their handmade products, promoting them on Instagram, and running targeted ads to attract customers who value craftsmanship.
Image Prompt:
A conceptual diagram representing the components of marketing: value creation, communication, and exchange. Use vibrant arrows connecting these components to show their interdependence.
Why Is It Important?
Marketing plays a pivotal role in shaping consumer perceptions and driving business success. A well-planned marketing strategy not only attracts customers but also retains them, creating a loyal customer base that contributes to sustained growth.

Why Is Marketing Important?
Marketing is not just about selling a product or service; it is the lifeblood of any business, enabling it to thrive in a competitive marketplace. Effective marketing ensures that a business can attract new customers, retain existing ones, and create a sustainable model for long-term success.
In today’s digital-first world, marketing is essential for businesses to stand out, communicate their value propositions, and build meaningful connections with their audience.
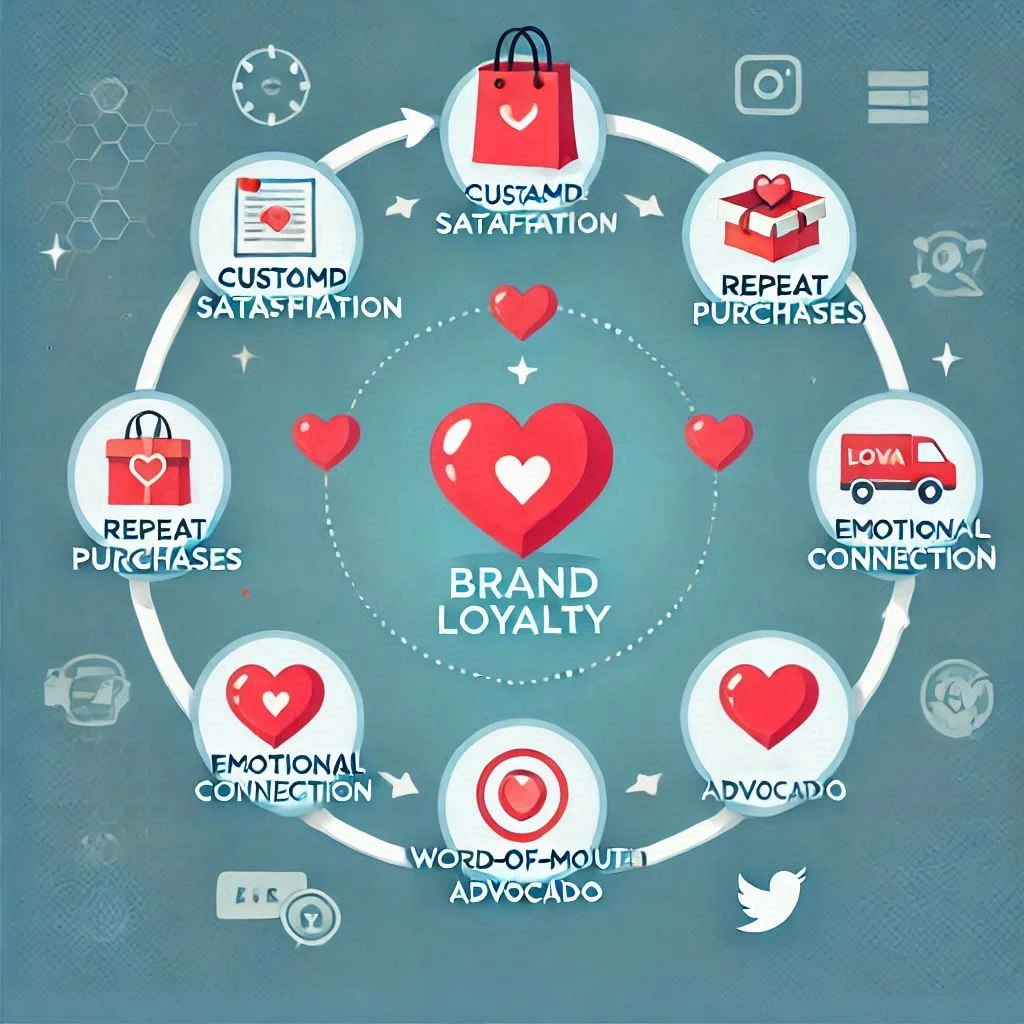
Building Brand Loyalty and Customer Relationships
- Fostering Trust
Marketing plays a vital role in creating trust between a brand and its customers. Consistent communication, delivering on promises, and showcasing genuine values are key aspects of building this trust. For instance, brands that actively engage with their customers on social media and provide timely support foster a sense of reliability. - Encouraging Repeat Purchases
Loyal customers are the foundation of a successful business. Marketing strategies such as personalized email campaigns, loyalty programs, and exclusive discounts ensure that customers feel valued, encouraging them to choose your brand repeatedly. - Creating Emotional Connections
Great marketing goes beyond transactions. It tells a story, evokes emotions, and creates lasting impressions. For example, campaigns that highlight sustainability or community involvement resonate deeply with customers who share those values. - Word-of-Mouth Advocacy
Satisfied, loyal customers often become brand advocates, spreading the word about your products or services organically. This form of marketing is invaluable as it builds credibility and trust among potential customers.
Guiding Smart Pricing Decisions
- Understanding Customer Perception
Pricing is not just about numbers; it’s about how customers perceive the value of a product or service. Marketing helps businesses gather insights into what their target audience is willing to pay, ensuring prices align with perceived value. - Market Research and Competitive Analysis
Through marketing, businesses analyze competitors’ pricing strategies and position their offerings accordingly. For example, if competitors offer premium pricing, a business may differentiate itself by offering a value-based alternative. - Dynamic Pricing Strategies
Modern marketing uses data-driven tools to implement dynamic pricing strategies. By monitoring demand, seasonality, and customer behavior, businesses can adjust prices in real-time to maximize profitability. - Educating Customers About Value
Marketing is essential for justifying pricing. For instance, a marketing campaign highlighting a product’s premium materials, superior craftsmanship, or unique features can persuade customers to pay higher prices.

Why It Matters
Marketing ensures that businesses not only attract customers but also build lasting relationships that drive profitability and growth. Smart pricing strategies informed by marketing insights maximize revenue while maintaining customer satisfaction, creating a win-win scenario for both the business and its audience.
Where Is Marketing Used?
Marketing is omnipresent in today’s interconnected world. From digital platforms to traditional media and various business environments, it is a versatile tool that serves diverse purposes. Each channel and strategy has its unique impact, ensuring that businesses can reach their target audience effectively.
Digital Platforms
Digital platforms dominate modern marketing due to their extensive reach and ability to target specific audiences. Here are the key areas:
Social Media (Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn)
Social media platforms have transformed marketing into an interactive and engaging process.
- Facebook: Ideal for broad demographics with tools like paid ads, groups, and pages for direct engagement.
- Instagram: Focused on visuals, it excels in influencer marketing, product showcases, and stories.
- LinkedIn: A professional platform used for B2B marketing, networking, and thought leadership.

Search Engines (Google, Bing)
Search engines are the backbone of digital marketing.
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization) ensures that businesses appear organically in search results.
- PPC (Pay-Per-Click) advertising places businesses at the top of search pages for relevant keywords.
Blogs and Content Platforms
Blogs and content platforms help businesses establish authority and provide value to their audience.
- Educational articles, guides, and case studies build trust and drive traffic.
- Platforms like Medium and personal blogs serve as tools for thought leadership and brand awareness.
Video Platforms (YouTube, TikTok)
Video content dominates digital engagement.
- YouTube: Ideal for tutorials, product reviews, and ads targeting a global audience.
- TikTok: A newer player focusing on short, engaging, and viral content aimed at younger demographics.

Traditional Media
Traditional media, while overshadowed by digital platforms, remains crucial for reaching broad audiences.
Television and Radio
- Television: Delivers mass reach and is effective for storytelling through commercials.
- Radio: Targets local audiences with cost-effective ads, especially during commute hours.
Print Media (Magazines, Newspapers)
- Magazines: Cater to niche audiences, such as fashion, technology, or travel.
- Newspapers: Offer credibility and reach diverse demographics, especially for local businesses.
Billboards and Direct Mail
- Billboards: Provide high visibility in strategic locations like highways and city centers.
- Direct Mail: Personalized marketing through brochures, flyers, or postcards that directly reach potential customers.

Business Environments
Marketing strategies vary depending on the business environment:
B2B Marketing
- Focuses on selling products or services to other businesses.
- Uses professional platforms like LinkedIn, webinars, and whitepapers to showcase expertise.
B2C Marketing
- Targets individual consumers and focuses on emotional appeal and convenience.
- Utilizes social media ads, influencer partnerships, and customer reviews for promotion.
E-commerce and Retail
- E-commerce: Leverages digital marketing tools like retargeting ads, email campaigns, and SEO to drive online sales.
- Retail: Combines in-store promotions with digital strategies like geo-targeted ads and loyalty apps.

Types of Marketing Strategies
Marketing strategies define the approach businesses use to attract and retain customers. The right strategy depends on the target audience, goals, and available resources. Two major categories are digital marketing strategies and traditional marketing strategies, both of which are indispensable in today’s competitive environment.
Digital Marketing Strategies
Digital marketing leverages online platforms to reach a broader and highly targeted audience. It’s measurable, cost-effective, and dynamic.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO is the process of optimizing a website to rank higher on search engines like Google.
- On-Page SEO: Optimizing website content, keywords, meta descriptions, and headers for search engine visibility.
- Off-Page SEO: Building backlinks and creating content that earns authority from external websites.
- Technical SEO: Ensuring website speed, mobile-friendliness, and structured data to enhance search engine crawling.
Key Benefits:
- Increases organic traffic.
- Builds long-term credibility and trust.

Social Media Marketing (SMM)
Social media marketing involves using platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn to connect with the audience.
- Paid Ads: Targeted campaigns to reach specific demographics.
- Organic Posts: Sharing valuable content to engage and inform followers.
- Influencer Collaborations: Partnering with individuals who have a strong online presence to promote products.
Key Benefits:
- Enhances brand awareness and customer engagement.
- Provides measurable results through analytics.

Email and Content Marketing
These strategies focus on delivering personalized and valuable content to the audience.
- Email Marketing: Sending newsletters, promotional offers, and updates to subscribers.
- Content Marketing: Creating blogs, infographics, videos, and eBooks to establish expertise and provide solutions.
Key Benefits:
- Builds strong relationships through consistent communication.
- Drives traffic and conversions by addressing customer pain points.

Traditional Marketing Strategies
Despite the digital shift, traditional marketing strategies remain effective for creating lasting impressions and reaching non-digital audiences.
Print Advertising
Print ads in newspapers, magazines, and brochures target specific local or niche audiences.
- Magazines: Ideal for targeting niche demographics.
- Newspapers: Effective for local businesses to reach a broader audience.
Key Benefits:
- Tangible and trusted by older demographics.
- Creates lasting impressions.
Event Marketing
Hosting or participating in events to directly interact with potential customers.
- Trade Shows: Showcasing products to a targeted industry audience.
- Workshops: Educating attendees about services while promoting brand expertise.
Key Benefits:
- Builds personal connections.
- Encourages word-of-mouth referrals.

Word-of-Mouth Promotions
Encouraging satisfied customers to recommend products or services to others.
- Often driven by exceptional customer experiences.
- Enhanced through referral programs offering incentives.
Key Benefits:
- Increases credibility as recommendations come from trusted sources.
- Cost-effective and organic.

What Are the 4 Ps of Marketing?
The 4 Ps of Marketing—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion—form the cornerstone of any successful marketing strategy. These elements guide businesses in developing, distributing, and promoting their products or services effectively, ensuring they meet customer needs and stand out in competitive markets.
Product
The product refers to what a business offers to its customers. It could be a tangible item, like electronics or clothing, or an intangible service, like consulting or software solutions.
Key Considerations:
- Features and Benefits: Define the product’s unique selling points (USPs). What problem does it solve?
- Design and Quality: Ensure the product aligns with customer expectations and delivers consistent quality.
- Lifecycle: Understand its lifecycle stages—introduction, growth, maturity, and decline—to plan marketing efforts accordingly.
Example:
Apple’s iPhones are marketed as premium devices with innovative features, sleek designs, and unmatched user experiences, making them a benchmark in the smartphone industry.
Price
Price is the cost customers pay for a product or service. It’s a critical factor in influencing customer purchasing decisions.
Key Considerations:
- Competitive Pricing: Compare prices with competitors to position yourself effectively.
- Value Perception: Ensure the price aligns with the perceived value of the product.
- Discounts and Offers: Use limited-time offers to attract price-sensitive customers without devaluing the product.
Pricing Strategies:
- Cost-Plus Pricing: Adding a markup to the production cost.
- Dynamic Pricing: Adjusting prices based on demand and market conditions.
Example:
Luxury brands like Rolex use premium pricing to convey exclusivity and prestige, attracting high-end consumers.

Place
Place refers to where and how customers access your product or service. It involves distribution channels and logistical decisions.
Key Considerations:
- Online vs. Offline: Decide whether to sell through physical stores, e-commerce platforms, or both.
- Distribution Channels: Use direct-to-consumer (DTC) models, wholesalers, or retailers based on your target market.
- Accessibility: Ensure the product is available in locations convenient for your target audience.
Example:
Amazon excels in ensuring product availability through its global e-commerce platform and fast delivery services.
Promotion
Promotion involves all activities aimed at communicating the product’s value to the target audience. It’s how you create awareness and persuade customers to choose your brand.
Key Promotional Channels:
- Advertising: TV, social media ads, and search engine marketing.
- Public Relations (PR): Building a positive brand image through media coverage.
- Sales Promotions: Limited-time discounts, coupons, and buy-one-get-one (BOGO) offers.
- Personal Selling: Engaging directly with customers to explain benefits and close sales.
Example:
Coca-Cola’s consistent promotional efforts, including seasonal campaigns and event sponsorships, keep its brand at the forefront of customers’ minds.

What Are the Benefits of Marketing?
Marketing plays a pivotal role in the success and sustainability of any business. By effectively implementing marketing strategies, businesses can achieve several advantages, such as increasing brand awareness, engaging customers, driving sales, and fostering long-term growth. Below, we delve into these benefits in detail.
Enhancing Brand Visibility
Brand visibility is the extent to which your target audience recognizes and remembers your brand. Strong marketing efforts ensure that your brand remains in the minds of consumers.
Key Tactics to Enhance Brand Visibility:
- Content Marketing: Sharing valuable and relevant information through blogs, videos, and social media posts to establish authority.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Optimizing your website to appear at the top of search results, making it more accessible.
- Social Media Campaigns: Using platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and LinkedIn to consistently engage with your audience and build brand recognition.
Real-Life Example:
Nike’s “Just Do It” campaign not only enhanced brand visibility but also associated the slogan with motivation and athleticism worldwide.

Driving Customer Engagement and Sales
Marketing creates meaningful connections between a brand and its customers, fostering trust and loyalty. Engaged customers are more likely to make purchases and recommend the brand to others.
Key Strategies for Engagement and Sales:
- Personalized Campaigns: Tailoring offers, emails, and recommendations based on customer preferences.
- Interactive Content: Quizzes, polls, and user-generated content encourage active participation.
- Social Proof: Highlighting customer reviews, testimonials, and case studies to build trust.
- Limited-Time Offers: Using discounts and promotions to create urgency and boost sales.
Real-Life Example:
Amazon uses personalized recommendations based on browsing history, significantly increasing conversion rates and customer satisfaction.

Supporting Long-term Business Growth
Marketing is not just about short-term gains; it lays the foundation for sustainable business growth by building strong customer relationships and positioning the brand as a leader in its industry.
Key Marketing Practices for Long-term Growth:
- Loyalty Programs: Rewarding repeat customers with exclusive perks.
- Thought Leadership: Sharing insights and expertise through blogs, whitepapers, and webinars to establish authority.
- Continuous Engagement: Regularly interacting with customers through newsletters, social media updates, and post-sale support.
Real-Life Example:
Tesla’s innovative marketing approach, including showcasing its technology and sustainability goals, has solidified its position as a market leader in electric vehicles.

Marketing for Small Businesses
Marketing is vital for small businesses aiming to establish their presence and compete in a dynamic market. Through innovative and budget-friendly strategies, small businesses can effectively reach their target audience, foster growth, and build customer loyalty. Here’s a comprehensive look at how small businesses can leverage marketing to thrive.
Try now Zooli.ai AI Digital Marketing SAS
How Small Businesses Use Marketing to Compete
Small businesses often face competition from larger corporations with substantial budgets. Strategic marketing enables them to level the playing field by focusing on niche markets and personalized customer experiences.
Effective Marketing Tactics for Competition:
- Targeted Niche Marketing:
- Focus on a specific audience segment to build a strong and loyal customer base.
- Example: A local organic bakery targeting health-conscious customers.
- Customer-Centric Services:
- Highlight personalized services and community involvement to build trust.
- Creative Social Media Campaigns:
- Use platforms like Instagram and TikTok to share relatable content that resonates with local audiences.
Real-Life Example:
A neighborhood coffee shop can compete with major chains by offering unique blends and hosting community events.

Importance of Digital Marketing for Local Businesses
Digital marketing is crucial for local businesses to expand their reach and connect with potential customers in their area.
Key Benefits:
- Enhanced Visibility:
- Optimize for local search with tools like Google My Business.
- Use location-based keywords to appear in “near me” searches.
- Cost-Effective Reach:
- Digital marketing offers a lower cost-per-lead compared to traditional methods.
- Social media ads allow precise targeting based on location, interests, and demographics.
- Engagement Through Reviews:
- Encourage satisfied customers to leave reviews, building credibility.
Real-Life Example:
A local plumber optimizing their Google My Business profile with reviews and accurate location details increases visibility in local searches.

Affordable Marketing Strategies for Small Businesses
Small businesses often operate on tight budgets, but that doesn’t mean marketing has to take a backseat. There are several affordable strategies that can yield impressive results.
Top Affordable Marketing Strategies:
- Social Media Marketing:
- Post regular updates, engaging content, and promotions on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
- Email Campaigns:
- Collect emails through website sign-ups and offer exclusive discounts to subscribers.
- Content Marketing:
- Write blogs that answer common customer questions to establish authority in the niche.
- Collaborations:
- Partner with other local businesses for cross-promotions.
- Referral Programs:
- Offer discounts or incentives to customers who refer your business to others.
Real-Life Example:
A local yoga studio running a referral program increases its customer base without significant ad spend.

FAQs About Where Marketing Is Used
Marketing is an essential tool for businesses across all sectors. Whether you’re a small startup or a large corporation, understanding where and how marketing is applied can help you stay competitive and achieve long-term success. Below are answers to some of the most common questions about where marketing is used.
What Are the Main Industries Where Marketing Is Used?
Marketing is a key driver across all industries, but it is especially significant in the following sectors:
- Retail and E-commerce:
- In this industry, marketing strategies are crucial for attracting new customers, building brand loyalty, and generating online and offline sales.
- Example: Online stores like Amazon and e-commerce platforms use digital marketing strategies like SEO, paid ads, and social media marketing to drive sales.
- Healthcare:
- Healthcare marketing is focused on building patient trust, promoting services, and educating the public on health-related issues.
- Example: Local clinics often use digital marketing to increase awareness of their services and build a loyal patient base.
- Technology:
- With rapid innovation, marketing in tech focuses on promoting cutting-edge products, educating potential customers, and maintaining a strong brand image.
- Example: Companies like Apple and Microsoft use product launches and influencer marketing to stay at the forefront of consumers’ minds.
- Education:
- Educational institutions use marketing to attract students, promote courses, and build their reputation.
- Example: Online learning platforms like Coursera and universities use digital ads, SEO, and social media to reach prospective students.
- Real Estate:
- Real estate marketing helps agents and developers connect with potential buyers and renters, showcasing properties and services.
- Example: Real estate companies use virtual tours, targeted Facebook ads, and SEO to market homes and apartments.

How Does Digital Marketing Differ from Traditional Marketing?
Digital Marketing and Traditional Marketing are two distinct approaches to reaching customers, each with its own strengths and limitations. Here’s how they differ:
- Reach:
- Digital Marketing allows businesses to target a global audience through platforms like social media, search engines, and email.
- Traditional Marketing focuses on local or regional audiences through TV, radio, print ads, and billboards.
- Cost:
- Digital Marketing is often more affordable and offers a better return on investment (ROI) because it targets specific customer segments.
- Traditional Marketing typically requires a larger budget, as TV ads or print media can be expensive to produce and place.
- Measurability:
- Digital Marketing allows for precise tracking and analytics (e.g., clicks, conversions, impressions), making it easier to measure success and adjust campaigns in real-time.
- Traditional Marketing is harder to measure, as there is no immediate feedback loop to track performance.
- Engagement:
- Digital Marketing enables direct engagement through comments, likes, shares, and emails.
- Traditional Marketing has limited interaction, as customers cannot directly respond to print or TV ads.

What Is the Most Effective Platform for Marketing in 2024?
As digital marketing continues to evolve, new platforms emerge, but some consistently stand out as the most effective in 2024.
- Social Media:
- Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook remain key platforms, allowing businesses to target specific demographics through paid and organic content.
- Example: Short-form video content on TikTok has become one of the most engaging forms of marketing.
- Search Engines:
- Google continues to be the leader for paid ads and organic traffic through SEO, making it a top choice for businesses to reach customers actively searching for products or services.
- Email Marketing:
- Email remains a powerful platform for driving conversions with personalized offers, newsletters, and customer loyalty programs.
- YouTube:
- Video content continues to dominate, and YouTube remains a powerful tool for brand storytelling, tutorials, and product demonstrations.
Real-Life Example:
Companies like Nike and Starbucks effectively leverage Instagram and YouTube to engage with younger, tech-savvy consumers.

Can Small Businesses Use the Same Strategies as Large Corporations?
While small businesses can certainly adopt many of the same marketing strategies used by large corporations, the implementation differs due to budget constraints and resources.
- Customization and Niche Marketing:
- Small businesses can focus on targeted niche marketing, tailoring content specifically to their community or unique audience, which is often more cost-effective.
- Example: A local bookstore using social media to promote niche books or community events.
- Budget-Friendly Tools:
- While large corporations may invest in big-budget ad campaigns, small businesses can use more affordable tools like social media marketing, Google Ads, and email campaigns.
- Personalized Customer Interactions:
- Small businesses can offer a more personalized experience, which large corporations may struggle to replicate due to their size.
Real-Life Example:
A small fashion boutique using Instagram stories and Facebook ads to engage directly with local customers is just as effective as large brands using mass-media ads.

Why Is Marketing Essential for E-commerce?
Marketing is crucial for e-commerce because it directly impacts visibility, customer acquisition, and retention. In the online world, where competition is fierce, effective marketing can help e-commerce businesses stand out.
- Customer Acquisition:
- E-commerce businesses rely on digital marketing strategies like SEO, paid ads, and content marketing to drive traffic to their online stores.
- Brand Awareness:
- Marketing helps e-commerce businesses build recognition in a crowded online marketplace.
- Retention and Loyalty:
- Email marketing, retargeting ads, and personalized offers help businesses retain customers and encourage repeat purchases.
Real-Life Example:
Amazon’s use of personalized recommendations and targeted ads ensures customer retention and continuous sales growth.

Conclusion
In conclusion, marketing is a powerful tool that drives success across diverse industries, helping businesses reach their target audience, build brand awareness, and foster customer loyalty. Whether through traditional channels like TV and print or digital platforms such as social media and search engines, marketing strategies are essential for both small businesses and large corporations. By understanding where and how marketing is used—whether it’s in local markets, e-commerce, or niche industries—businesses can craft tailored approaches that not only engage customers but also fuel long-term growth. As marketing continues to evolve, embracing both digital and traditional methods, along with staying updated on emerging platforms, will empower businesses to stay competitive and achieve their marketing goals effectively.

